What is Technology? Understanding Its Evolution and Impact
Introduction to Technology

Technology is an integral part of our daily lives, influencing how we communicate, work, and entertain ourselves. But what exactly is technology? At its core, technology is the application of scientific knowledge for practical purposes, particularly in industry. It encompasses a wide range of tools, machines, systems, and processes designed to solve problems and enhance human capabilities.
Content
Evolution of Technology
The history of technology is a story of human ingenuity and innovation. From the discovery of fire to the development of the wheel, humans have always sought ways to improve their lives through technological advancements. The evolution of technology can be broadly categorized into several key periods:
Ancient Technology
- Stone Age Tools: The earliest humans used simple tools made of stone, wood, and bone.
- Agricultural Revolution: The invention of farming tools and techniques allowed for settled communities and food surplus.
Industrial Revolution
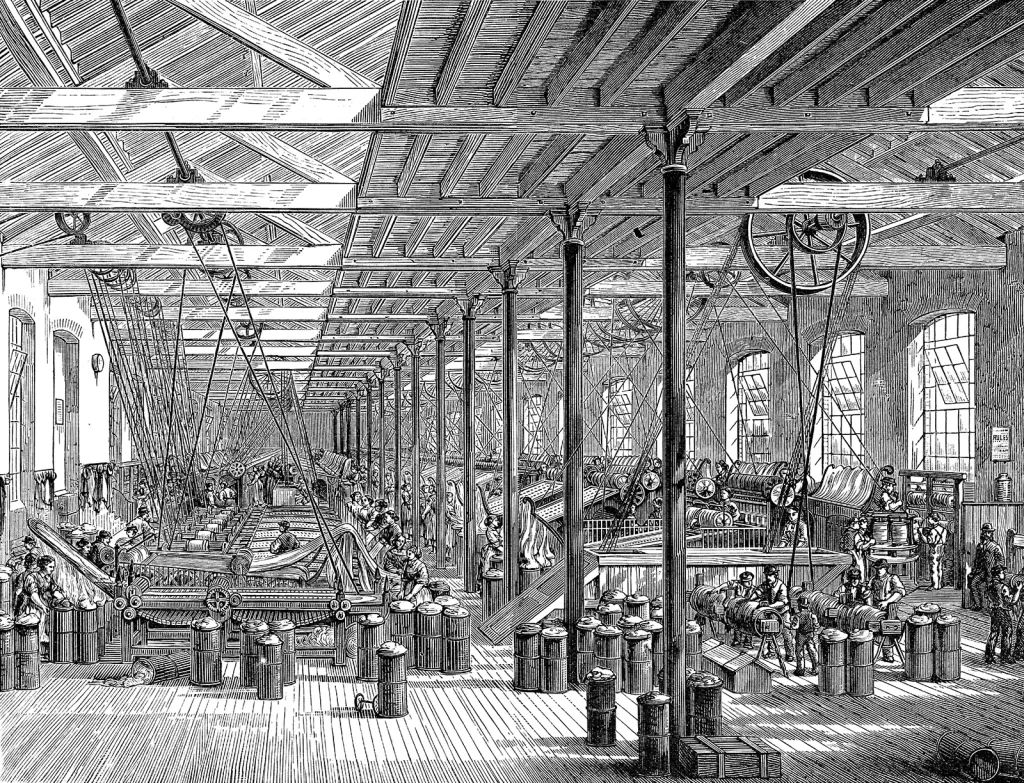

- Steam Engine: The development of steam-powered machines revolutionized transportation and manufacturing.
- Mass Production: Innovations like the assembly line enabled mass production of goods, reducing costs and increasing availability.
Digital Revolution
- Computers and Internet: The invention of computers and the internet transformed communication, information access, and business operations.
- Mobile Technology: The advent of smartphones and tablets has made technology portable and accessible anywhere.
Recommended for you: The ABCs of Garage Door Replacement: A Step-by-Step Guide
Types of Technology
Technology can be classified into various categories based on its application and functionality. Here are some major types of technology:
Information Technology (IT)
- Computers: From desktops to laptops, computers are essential for processing and storing data.
- Internet: The global network that connects millions of computers, facilitating communication and information exchange.
Biotechnology

- Genetic Engineering: Techniques like CRISPR allow for precise modification of DNA to treat diseases and improve crops.
- Pharmaceuticals: Advances in biotechnology have led to the development of new drugs and therapies.
Energy Technology
- Renewable Energy: Solar, wind, and hydroelectric power are sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels.
- Energy Storage: Innovations in battery technology are crucial for storing energy from renewable sources.
Communication Technology
- Telecommunication: Mobile phones, satellites, and fiber optics enable instant communication across the globe.
- Social Media: Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram have transformed how we interact and share information.
Impact of Technology on Society
Technology has had profound effects on various aspects of society, bringing both benefits and challenges.
Economic Impact
- Productivity: Technology increases efficiency and productivity in industries, leading to economic growth.
- Job Creation: New technologies create jobs in fields like IT, biotechnology, and renewable energy.
- Job Displacement: Automation and artificial intelligence can lead to job loss in certain sectors.
Social Impact
- Communication: Technology has made it easier to stay connected with friends and family, regardless of distance.
- Education: E-learning platforms and digital resources have made education more accessible.
- Privacy Concerns: The widespread use of technology raises issues related to data privacy and security.
Environmental Impact
- Pollution: Industrial technology has contributed to environmental pollution and climate change.
- Conservation: Advances in technology are also being used to monitor and protect natural resources.
Future of Technology
The future of technology promises even more transformative changes, with emerging technologies poised to revolutionize various fields.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Machine Learning: AI systems that can learn and adapt are being developed for applications ranging from healthcare to finance.
- Automation: AI-driven automation is expected to increase efficiency in manufacturing, logistics, and other industries.
Internet of Things (IoT)
- Smart Devices: IoT technology connects everyday objects to the internet, enabling them to communicate and share data.
- Smart Cities: IoT can be used to manage urban infrastructure, improve traffic flow, and enhance public safety.
Quantum Computing
- Supercomputing: Quantum computers have the potential to solve complex problems much faster than classical computers.
- Cryptography: Quantum computing could revolutionize data encryption and cybersecurity.
Space Exploration

- Space Travel: Advances in rocket technology and space travel are making it possible to explore other planets.
- Satellite Technology: Satellites play a crucial role in communication, weather forecasting, and Earth observation.
Also, Read this post: E-Commerce Evolution: Embracing Bitcoin for Quick and Secure Shipping Labels
Conclusion
Technology is a dynamic and ever-evolving field that has a profound impact on our lives. From ancient tools to modern AI, technology continues to shape our world and drive progress. As we look to the future, it is essential to harness the potential of technology responsibly, ensuring it benefits society and the environment.
FAQs about Technology
What is the definition of technology?
Technology is the application of scientific knowledge for practical purposes, involving tools, machines, systems, and processes to solve problems and enhance human capabilities.
How has technology evolved?
Technology has evolved from simple tools in the Stone Age to complex digital systems in the modern era, including the Industrial Revolution, the Digital Revolution, and emerging technologies like AI and quantum computing.
What are the major types of technology?
Major types of technology include information technology (IT), biotechnology, energy technology, and communication technology, each serving different purposes and applications in society.

Shawn Davis is a wonderful person. He is very nice and always willing to help out! He loves his job because it lets him share interesting things with people who want to know about new developments in the world of technology.












